
In the example shown in Fig 3 (overpressure) it would be necessary to move such hazards more than 0.4m away from the energy source. Vulnerable objects should be positioned outside the high-pressure radius. (see CalQlata's Engineering Principles, Velocity & Acceleration and Shock Load calculators) Insert the mass of the object (m) and the velocity of the pressure wave (v) into the fomula and you have a launch energy (E) that can be used to determine its flight trajectory along with the damage it could do to an impacted body If you know the velocity of the pressure wave on an object of mass 'm' you can calculate its launch energy from a modified version of Morison's equation This threat is generally responsible for most of the damage/injury caused to property/personnel from an explosion. The overpressure generated will break and/or propel objects positioned close to the energy source. In the example shown in Fig 3 it would be necessary to move such hazards more than 1m away from the energy source. Risk of damage from excess temperature can be avoided by moving flammable materials and substances out of the vulnerable radius. However, as can be seen in Fig 3 (temperature) this risk is highly localised. The air pressure during an explosion is initially very high ( Fig 3) and any combustible materials with a lower flash-point than the temperature generated by this pressure will of course ignite if exposed to a spark or flame. The pressure from multiple explosions occurring in the same vicinity but separated by time may be superimposed but shifted according to their radial-time shift ( Fig 2). Given that an explosion is simply the release of energy, more than one energy source exploding at the same time can be included in the final pressure wave profile by simply adding them together. This vacuum will ultimately fill with atmospheric gas when the pressure wave has lost most of its momentum. deep water) and non-existent if released into a vacuum.Įxplosions can be generated from an atomic/chemical reaction or the release of a pressurised gas, both of which will result in a rapidly expanding spherical pressure wave of compressed air radiating away from the source and leaving a partial vacuum at its centre ( Fig 1).

As is the case for a pressure wave generated in an atmosphere with an energy density (pressure) greater than or close to that of the explosion (e.g. Explosion (a definition)Īn explosion is the sudden release of energy into an atmosphere in which it cannot be contained, and as with shock loads this can be anything from 1 Joule to many mega-Joules it's all a matter of degree. You can find formulas for each parameter below the calculator.Whilst Explosions is perfectly useable as a stand-alone calculator in that it provides all the useful properties of a pressure wave resulting from an explosion, it has been designed primarily to provide the input data for CalQlata's Vents programs that will define the minimum dimensions for vents and apertures for enclosed spaces according to various standards and specifications, such as the NFPA. The calculator allows users to easily convert between different units of measurement, making it a versatile tool. While the formula is not very hard, you can easily make errors by using wrong units, for example, revolutions per second instead of radians per second, centimeters instead of meters, and so on. If the cord’s length is 50 cm, what is the centripetal force?

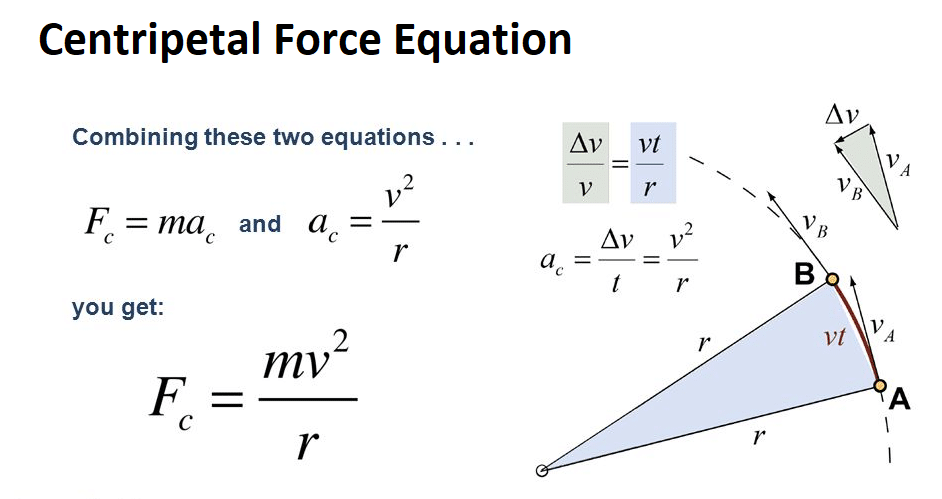
Here is an example of such problem: A 500-gram ball, attached to the end of a cord, is revolved in a horizontal circle with an angular speed of 5 rad/s. It can be used to calculate the force required to maintain an object in circular motion, the mass of an object moving in a circular path, the radius of a circular path required to maintain an object in motion at a certain speed, and the velocity required to maintain an object in a circular path of a certain radius. The calculator allows users to input any three known parameters and calculate the unknown parameter, making it an excellent tool for solving physics homework problems. The formula states that the force required to maintain an object moving in a circular path is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the square of its velocity, divided by the radius of the circular path.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
